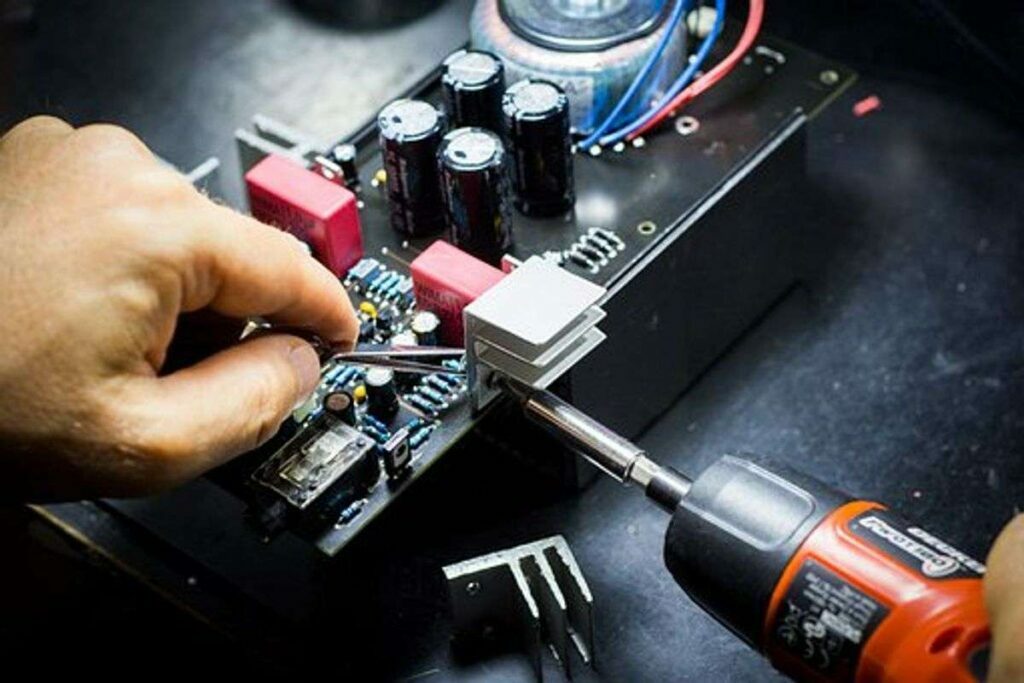
In 1936, the first printed rounds board (PCB) was created using Paul Eisle. But it wasn’t until the 1950s when the United. S. Defense industry began integrating PCBs in their explode detonator systems that paper circuit boards found vast application. PCBs are now utilized in nearly all manufactured products, including automobiles, cellular telephones, and notebooks. Select the Best Pcb.
A Summary of the PCB Fabrication Processes
PCBs usually are initially fabricated with the use of two different types of software. Computer Made it easier for Design (CAD) software to design the electronic schematic of the circuit to be made. After the schematic is designed, Laptop or computer-Aided Manufacturing (CAM) applications are used by engineers to produce often the PCB prototype.
Once the PCB prototype is designed, the first step inside the fabrication process is to opt for the material of the printed rounds board. There are many different types of PCB materials available.
Still, the common ones, based on the application and a customer’s requirements, include Alumina, Arlon, Bakelite, CEM1, CEM5, Ceramic, FR1, FR4, FR4 High Temperature, GeTek, Nelco, Polyimide, and Rogers. The design qualification dictates the dimensions with the PCB (I. e., period, width, and thickness).
Once the material has been selected, the 1st process is to apply any coating of copper for the entire board. The standard layout will then be printed around the board by a photosensitive method.
Then, a photo engraving method will be used so that all the birdwatcher that is not part of the circuit structure will be etched out or perhaps removed from the board. The cake you produced copper creates the footprints or tracks of the PCB circuit. To connect the routine traces, two processes are employed.
A mechanical milling method will use CNC machines to eliminate the unnecessary copper from your board. Then, an etch-resistant, silk-screen printing process will be applied to cover the locations where traces must be present.
In the PCB manufacture process, the PCB table contains copper traces without the circuit components. To install the components, holes must be drilled at the points where the power and electronics parts fit on the board. The openings are prepared with both lasers or a special drill bit made of Tungsten Carbide.
Once the holes are usually drilled, hollow rivets typically are inserted into them as well as they are coated by the electroplating process, which makes the electrical connection between your layers of the board. A new masking material is then used on the coat of the entire PCB except for the pads and the holes.
There are various types of masking material including, lead solder, lead no cost solder, OSP (Entek), deep/hard gold (electrolytic nickel gold), immersion gold (electroless ni gold – ENIG), cord bondable gold (99. 00% pure gold), immersion gold, flash gold, immersion pan (white tin), carbon tattoo, and SN 100CL, an alloy of tin, water piping, and nickel. The PCB fabrication process’s final step is to screen print the board so labels and the star appear at their proper spots.
Testing the Quality of the PCB Board
The board needs to be tested to verify its functionality before placing the electrical power and electronic components about the PCB. In general, there are two styles of malfunctions that can produce a faulty PCB: a short or even an open.
A “short” is a connection between two or more signal points that should not be found. An “open” is a stage where a link should be seen but does not. These problems must be corrected before the PCB is assembled. Unfortunately, a few PCB manufacturers do not examine their boards before they may be shipped, leading to issues at the customer’s location.
Therefore quality testing is a necessary process of the PCB manufacturing process. Testing ensures the PCB boards are in proper working condition before element placement.
Read Also: 7 Popular Computer Degrees for IT Jobs